Roller vs. Ball-Bearing vs. Friction Slides

Equipment supported by slides, also known as runners or telescopic rails. These rail-based components help equipment pull out from a stationary structure, allowing it to glide outward while being supported by the slides. The slides will facilitate this outward movement process with the help of ball bearings or rollers, but these are only two of the most common types of telescopic slides, finding use in storage units, trays, electronic equipment, among others.
Each type has its own advantages, making it suitable for different uses. Understanding these distinctions will help you choose the right mechanism for your application.
What Is a Drawer Slide?
What Is a Drawer Slide?
Telescopic slides are mechanisms attached to a stationary structure and moving equipment, creating smooth outward opening and closing functions. The moving part of this slide mechanism is mounted onto the equipment itself, whereas the non-moving part sits opposite, mounted onto the stationary structure. Aside from ball-bearing and roller slides, other common types of telescopic slides include:
- Undermount telescopic slides that are mounted below the extending unit for use in medical, vending, industrial, and electronic industries.
- Friction slides without ball bearings or rollers provide solutions where dusty environments or limited number of opening & closing are expected.
- Full-extension telescopic slides that extend outward to 100% of closed slide length.
- Three-quarter extension telescopic slides that open up to 75% of the slide closed length
- Locking telescopic slides with latches, buttons, or levers that make them ideal for mobile applications. Locking is possible in full closed and / or fully open positions
- Push-to-open telescopic slides that open with a gentle push inward then can be extended outward.
- Side-mount telescopic slides that come in a variety of styles, including roller, friction, and ball-bearing moving members.
- Soft-close telescopic slides that use a spring to simplify the closing drawers or equipment
What Is a Roller Drawer Slide?
Slides with rollers as opposed to ball bearings, offer the ability to interchange equipment into stationary mounted slides. Removal of the stationary mounted slides is not required. As the drawer is extended or retracted, these roller wheels support the moving equipment while the remaining stationary slide members use ball bearings. When the mechanism extends or retracts, the equipment supported slide members with rollers are engaged within its mating slide member to provide stable friction free movement.
What Is a Ball-Bearing Slide?
Ball-bearing slides use ball bearings within slide member rails, to support the equipment during the open or closing functions. Their construction reduces friction between moving parts to create effortless sliding. These will be found in applications such as Military or Commercial Electronics, Tool Storage, Vending, Office Furniture, Industrial Vehicles, and other applications where increased loads need to move outward and inward. Drawer slides with ball bearings offer more flexibility and have a life expectancy greater than friction or roller type slides, with a typically higher load rating and flexible orientation. Unlike friction or roller type slides, interchanging equipment into another stationary mounted slide member is not recommended.
What is a Friction Slide?
Friction slides do not use either ball-bearing or rollers in their construction. Interlocking slide members glide along with each other as a partial or full travel device. Friction slides are also known as Solid Bearing Slides. Friction slides are well suited to operate in dusty environments, allow interchanging of slide members, and provide a method to fully support a drawer / chassis overall length. Friction slides are ideal solutions for tool box, vending machine trays, and electronic chassis applications.
How Do They Compare?

Ball-Bearing Slides
The key factors for choosing ball-bearing slides include:
- Construction: Ball-bearing slides use ball bearings within a track / raceway / ball-race providing consistent movement.
- Load capacity: These slides can support high loads and are used in applications to provide a stable mounting method between a stationary structure and item being withdrawn or to provide movement for servicing or operating with low amount of pull force.
- Operational smoothness: The ball bearings offer precision slide movement, low pull-out / push-in forces, and in operation provide a stable means to bring a load outward and inward.
- Orientation: Ball-bearing slides are more flexible in orientation, as they are fixed to
- the grooves of each sliding mechanism. They can be used in either vertical or horizontal configurations depending on drawer loads or amount of space available within the stationary structure and moving unit.
- Mounting: There are 5 different methods to mount slides to the final application
- Vertical Side Mount, mount to both sides of drawer
- Undermount, flat mounted to bottom of drawer
- Undermount, vertically mounted to bottom of drawer
- Same-side-mount, vertical slides mounted to same side of drawer
- Upper Guide, flat mounted to top of drawer to provide stabilization in conjunction with the main load carrying slides
- Cost: These often have a lower price point as compared to Roller Slides
Roller Slides
Considerations when looking at roller slides include:
- Construction: These slides use a combination of individual roller bearings on the moving drawer member and ball bearings on the stationary cabinet slide member. Typically made of carbon or stainless steel, the rollers are placed within the slide to carry expected loads with smooth and accurate movement. The construction allows the drawer members to be exchanged with other stationary slide members.
- Load capacity: Loading capacity is generally 250 pounds / 110 kilograms or less per pair.
- Operational smoothness: Compared to ball bearing slides, the operational smoothness is same as ball bearing slides depending on unit physical weight and location of drawer center of gravity.
- Orientation: Typically mounted to both sides of drawer, available options include both straight pull-out & inward or allows the drawer to pivot upward or downward for access to either the top or bottom of chassis, when slide is fully extended outside of stationary structure. These slides are not designed to be mounted as flat undermount, below drawer.
- Cost: Pricing is generally similar to ball bearing slides depending on selected slide material, aluminum or carbon steel
Friction Slides
Considerations when looking at roller slides include:
- Construction: slide members are formed to allow direct engagement to each other, provide out-ward and in-ward movement of drawer, and does not use rollers or ball bearings. These slides are commonly referred to as “solid bearing” slides.
- Load capacity: The load capacity is based on the pair of slides accepting the application intended load up to point where the drawer load exceeds the ability to extend or retract the slide members. The pair of slides will accept a 2X safety applied load in the slides fully extended position.
- Operational smoothness: Depending on drawer load to be supported, the movement forces will be greater than either ball bearing or roller bearing slide construction. The lack of ball bearings or roller bearings make the friction slides an ideal choice when dealing with dusty environments or with applications with a low frequency of outward and inward operation
- Orientation: Typical installations are slides mounted to either side of drawer. These slides can also be flat mounted to bottom of drawer or flat mounted to top of drawer to act as guide rather than as a load carrying slide. Slides can be hard mounted between drawer and stationary structure or with added adapter brackets can be installed into electronic racks.
- Cost: The slide pair will be less than aluminum constructed slides or stainless slides. Friction slide will be approximately the same as ball bearing or roller slides using carbon steel construction
Selection Tips
Choosing between roller and ball-bearing slides depends on your needs. Consider the items stored and the frequency of cabinet use to determine which telescopic slide rails will suit the application. Also, find out what guide rail lengths are available for telescopic slides — ball-bearing drawer slides often feature a longer guide rail length as there is a bigger contact area between mechanisms, giving these slides more stability when they are fully extended. Roller slides on the other hand, commonly come in shorter lengths to contribute to their cost-effective properties.
What Are the Care and Maintenance Requirements?
Taking care of telescopic slides, whether they are roller or ball-bearing, can extend the life span and lead to seamless operation. General care and maintenance tips for these mechanisms include:
- Weight capacity: Roller slides are designed for indicated load carry, per pair. Slides will accept a 2X overload condition at the fully extended position.
- Check for wear: Typically roller slides do not need to be “checked for wear” as the combination of rollers and ball bearings will provide smooth movement throughout the life of the intended application.
- Keep it clean: No cleaning is needed for the slides during the life of the intended application.
- Lubricate: Not required.
- Proper installation, hard mounted: Slides are installed on either side of the drawer with alignment to each other, having the correct space available between the drawer and cabinet structure. Cabinet opening width and tolerances and drawer width and tolerances are key to allow the slides to function.
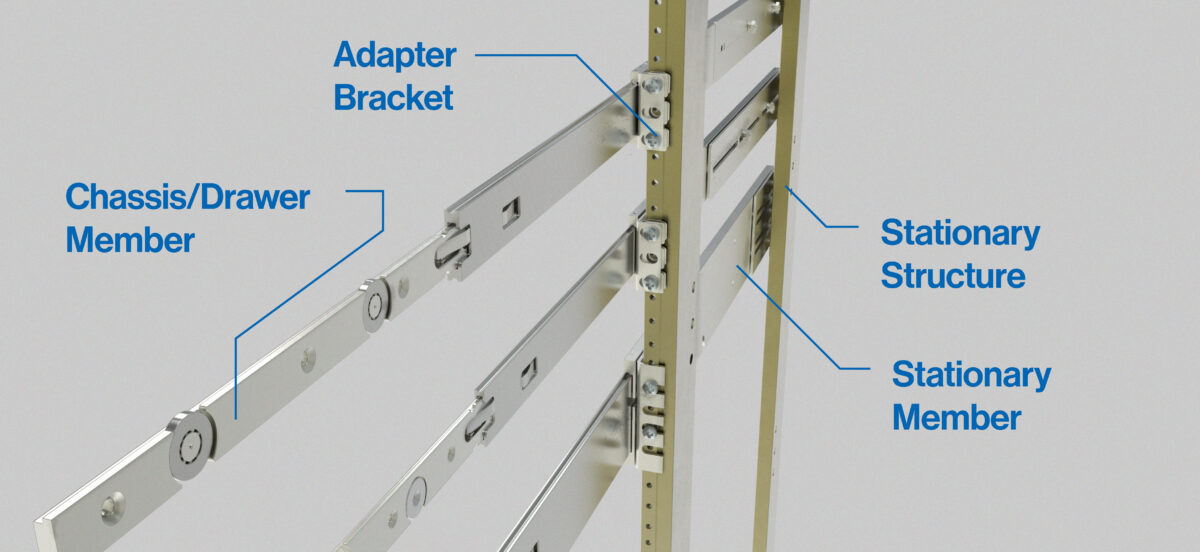
- Proper installation, electronic rack mounted: slides mounted to this style of stationary structure (rack) consists of adding adapter brackets to the slide body to attach to vertical mounting rails on stationary structure. When installing these slides with adapter brackets it is recommended the slide fixed member is separated from the drawer member. Install slide drawer members to either side of the drawer. Install the remaining slide cabinet members to cabinet but do not tighten the adapter brackets to cabinet structure fully. Extend the cabinet mounted slides, bring the chassis to mate with the extended member. Move the chassis in-ward and out-ward several times to allow the slides to align with each other, then fully tighten all cabinet mounted adapter brackets.
Shop Premium Quality Roller and Ball-Bearing Drawer Slides From Jonathan Engineering Solutions
Comparing ball-bearing vs. roller drawer vs. friction slides? All offer reliable support and smooth operation of various applications. Roller slides offer interchanging of drawers into alternate cabinets. Roller Slides also allow the drawer to rotate up or down depending the application and slide model selected. Drawer slides with Ball Bearings are ideal for high cycle applications as they are highly durable, offering precision and smooth operation consistently. Drawer slides with Friction Slides installed will provide outward access to equipment in a straightforward manner with excellent ability to interchange a drawer with other stationary mounted slides.
At Jonathan Engineered Solutions, we offer both Standard Catalog / COTS part numbers or have the ability to create custom telescopic slides for your project’s needs — whether that includes roller, friction, or ball-bearing slides. As a manufacturer with ISO 9001 and AS 9100 certifications, we provide you with high-quality telescopic slides with various extension ranges made from aluminum, stainless steel or carbon steel.
Contact us today to place your order or for assistance with your custom-engineered products.

Speak with a Sales Representative
Our representatives have a wealth of knowledge on all our products – let them steer you in the right direction.
Learn More